Secure Boot STM32MP1
STM32MP157C devices
Overview
Enabling secure boot in a device is an irreversible process. We recommend to skip actual testing for now.
If you make a mistake or lose the keys, you will brick your device.
The diagram below illustrates the trusted boot chain on the STM32MP15 (source:https://wiki.st.com/stm32mpu)
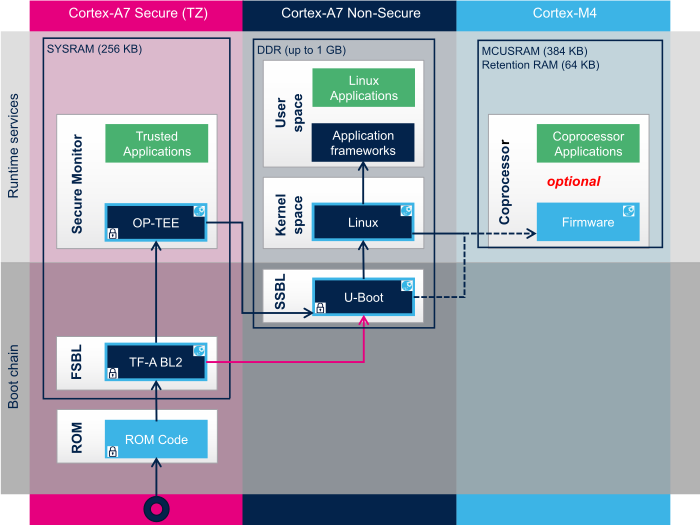
ROM code starts the processor in secure mode. It supports the FSBL (Trusted Firmware A) authentication and offers authentication services to the FSBL.
BootROM authenticates FSBL image using image signature; public key and ECDSA algo stored in STM32 header of the image. It performs an additional check to confirm that the public key from the image corresponds to the public key hash.
For additional details check ST's Boot chains overview
Authentication
(source: https://wiki.st.com/stm32mpu/)
STM32 MPU provides authentication processing with ECDSA verification algorithm, based on ECC. ECDSA offers better results than RSA with a smaller key. STM32 MPU relies on a 256 bits ECDSA key.
Two algorithms are supported for ECDSA calculation:
- P-256 NIST
- Brainpool 256
The algorithm selection is done via the signed binary header, as shown in STM32 header (subchapter in this same article). The EDCSA verification follows the process below:
It is also possible to sign/authenticate next level images using the same key pair. BootROM does provide services to FSBL (TF-A) for further image verification. It is possible to verify images of the whole chain of trusted bootloaders/firmware up to the first non-secure bootloader (U-Boot):
- TF-A Secure Monitor (BL31)
- OP-TEE (BL32)
- U-Boot (BL33)
This is done by invoking BootROM exported function (boot_context->p_bootrom_ext_service_ecdsa_verify_signature()).
For additional details you can check the sources for Trusted Firmware A, implementation of check_authentication() function in plat/st/common/stm32mp_auth.c (ST TF-A fork):
Key generation
Secure boot requires two different keys, one to sign the tfa partition(FIP) and uboot. The key to sign the FIP partition is:
tools/dk2/generate_keys.sh
This script will also generate the "plain" version of the privateKey called privateKey_noenc.pem that is used as a root of trust for the trusted firmware. Moreover, the script would generate a publicKeyhash that will be copied to the boot partition. This hash is important as it is what the ROM-CODE uses to validate the FIP partition signature.
The script to sign uboot, which consist of signing every element defined as part of the device tree that is loaded by the kernel. This script is located in:
tools/uboot/gen_keys.sh
Buildroot configuration
We are analysing how to provide an alternative signer based on Ledger Nano S device as part of the next Milestone. This will greatly simplify the key provision and signing process. Moreover, it provides additional security with respect to key storage.
Configuring secure-boot in buildroot is relatively easy, the configuration file for stm32 lives in the configs dir.
configs/zondaxtee_stm32mp157_dk2_defconfig
This file tells Buildroot what features it should enable when compiling inner libraries, by setting some per-package ENV variables. Secure boot in arm-based STM boards requires compile the arm trusted firmware with support for firmware authentication, and also it should load the root-of-trust key that is used to authenticate signed partitions. It is done through the BR2_TARGET_ARM_TRUSTED_FIRMWARE_ADDITIONAL_VARIABLES variable in the configuration file, that contains the following:
BR2_TARGET_ARM_TRUSTED_FIRMWARE_ADDITIONAL_VARIABLES="OPENSSL_DIR=$(HOST_DIR)/usr GENERATE_COT=1 TRUSTED_BOARD_BOOT=1 \
ROT_KEY=$(BR2_EXTERNAL_ZONDAXTEE_PATH)/keys/tfa_keys/privateKey_noenc.pem MBEDTLS_DIR=$(MBEDTLS_DIR) \
STM32MP_SDMMC=1 AARCH32_SP=optee DTB_FILE_NAME=stm32mp157c-dk2-mx.dtb STM32MP_USB_PROGRAMMER=1 \
BL33_CFG=$(BINARIES_DIR)/u-boot.dtb ARM_ARCH_MAJOR=7 ARCH=aarch32 PLAT=stm32mp1"
The more important settings here are:
GENERATE_COT=1
TRUSTED_BOARD_BOOT=1
ROT_KEY="which must point to the unencrypted private key used to sign
the partitions"
although the other settings are also important.
Signing Images
The signing process is implemented as an step in the build process. Buildroot defines some hooks that developers can use to run custom scripts. The hooks we use are:
- BR2_ROOTFS_POST_IMAGE_SCRIPT
- BR2_ROOTFS_POST_BUILD_SCRIPT
We use the POST_BUILD_SCRIPT hook to run our custom signing script, which signs the trusted firmware partition called FIP and uboot. This script calls the sign_tfa.sh and sign_uboot.sh scripts which are located under the board/zondax/stm32mp/ directory. Those scrips will look at the keys directories to get the private keys to sign their corresponding partitions, if those directories do not exist or are empty, they will generate new keys.
Deploying Keys
We mentioned in previous sections that there is a publicKeyhash that is
copied to the bootfs partition, and this key is used by the
ROM-CODE to authenticate the FIP partition. In order to accomplish
this, the ROM code reads a special register called OTP(one time
programable register) which contains up to 31 words. The publicKeyhash
must be written into this register, words 24 to 31, Otherwise the
authentication process would fail. In order to do this, we need to boot
our board with a signed image, while having a serial-port connection
active using Minicom. During the boot process, We can get into the uboot
console, by pressing any key. You have to pay attention to the boot
process to catch the prompt indicating that you can hit a key to stop the
autoboot:
DRAM: 512 MiB
Clocks:
- MPU : 650 MHz
- MCU : 208.878 MHz
- AXI : 266.500 MHz
- PER : 24 MHz
- DDR : 533 MHz
WDT: Started with servicing (32s timeout)
NAND: 0 MiB
MMC: STM32 SD/MMC: 0, STM32 SD/MMC: 1
Loading Environment from MMC... OK
In: serial
Out: serial
Err: serial
Net: eth0: ethernet@5800a000
Hit any key to stop autoboot: 0
STM32MP>
The prompt STM32MP indicates you are already in the uboot console, where we can make use of special commands to read/write the OTP register.
Load into RAM the publicKeyhash
The publicKeyhash is stored in the boot partition, in order to write it into the OTP register, We need first to load it into a secure ram, to do so, run the following command in the uboot console:
STM32MP> ext4load mmc 0:4 0xc0000000 publicKeyhash.bin
Now, verify that it was parsed correctly by reading the OTP values:
STM32MP> stm32key read 0xc0000000
OTP value 24: 1ce94f90
OTP value 25: 971d082f
OTP value 26: d443cf29
OTP value 27: f7c345d4
OTP value 28: 14873635
OTP value 29: b288ad40
OTP value 30: 38841b57
OTP value 31: b7a16954
Check if values are the same as in file in your clone of our repo (take into account BE/LE order):
$ hexdump keys/tfa/publicKeyhash.bin
0000000 e91c 904f 1d97 2f08 43d4 29cf c3f7 d445
0000010 8714 3536 88b2 40ad 8438 571b a1b7 5469
0000020
Once you confirm that the keyHash are the same you can close the device, which means that the device would boot only signed images with that particular key. If the image was either signed with a different key or not signed at all, the device won't boot and will blink a red led near the USER bottom.
Fuse the hash:
STM32MP> stm32key fuse -y 0xc0000000
And close the device:
STM32MP> stm32key close
After fusing the hash, you'll never be able to change the key. Even though, if you don't close the device you'll still be able to boot any image.
After closing the device, you'll definitely force your device to only boot images signed with the key you fused and NEVER boot any other image.
Reset device and check boot log on a serial output. It should contain Boot authentication Success notice:
NOTICE: CPU: STM32MP157CAC Rev.B
NOTICE: Model: STMicroelectronics STM32MP157C-DK2 Discovery Board
NOTICE: Board: MB1272 Var2 Rev.C-01
NOTICE: Boot authentication Success